Skin Pigmentation Disorders : Everything You Should Know
Are you worried about losing the pigment of your skin? Do you want to find out more information on skin pigmentation disorders? If your answer to either of these two questions is yes, you should definitely keep on reading.
In the paragraphs that follow, we will discuss melanin, the pigment of the skin and its important functions. Then, we will proceed to describe the most common skin pigmentation disorders, along with a number of remedies to treat them (if possible).
Melanin, skin pigment
It is common knowledge that the color of the skin is determined by melanin, a pigment produced by melanocytes. These are specialized cells, responsible for determining the amount of melanin that is present in a person’s skin. This pigment is, however, responsible not only for the color of the skin but also for the one of the hair and eye iris. The quantity of melanin in a person’s skin varies according to race and amount of sun exposure.
The latter is particularly important, as the constant exposure to the sun stimulates the production of melanin. This is actually a form of protection against the harmful action of UV rays. It is also worth mentioning that there are a number of factors that can affect the production of melanin at the level of the skin, with hormonal changes standing at the top of the list.
Skin pigmentation disorder, more common than you think
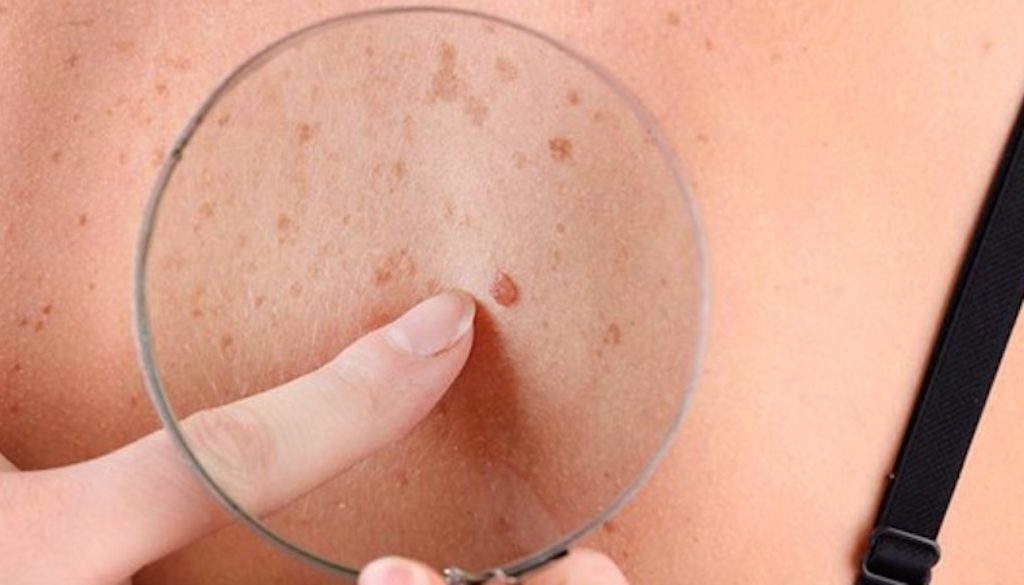
All over the world, there are millions of people who suffer from a skin pigmentation disorder. In some cases, as you will have the opportunity to read below, the pigment of the skin is lost forever and cannot be recovered. In other cases, the loss of pigment is only temporary and, with the right treatment approach, the skin can return to normal. Now, let’s proceed and find out more information about some of the most common diagnosed skin pigmentation disorders.
Albinism, total or partial loss of pigment
Albinism is a rare skin pigmentation disorder, being genetically inherited (transmitted from one generation to the other). As mentioned above, it is defined by the total or partial loss of skin pigment. People are born with albinism and their skin & hair color is different from the rest of the family members. The hair is white and the skin is pale, plus the eyes are pink. Unfortunately, there is no cure for albinism. People who suffer from this condition are recommended to avoid exposure to the sun, due to the fact that they lack the necessary skin pigment to protect themselves against the harmful action of UV rays.
Melasma, the mask of pregnancy
Melasma is a skin pigmentation disorder that commonly appears in women who are pregnant, hence the denomination as the mask of pregnancy. It is characterized by symmetric areas of hyperpigmentation that appear at the level of the face, dark-brown in color. According to the specialists in the field, there are a number of factors that contribute to the appearance of melasma, including hormonal changes, sun exposure or oral contraceptive pills.
The condition can be improved by using skin brightening creams or with more invasive treatments, such as chemical peels or laser resurfacing. Patients are recommended to apply sunscreen with high SPF when going out and, if possible, to avoid sun exposure (this will prevent the condition from aggravating).
Pigment loss & skin damage
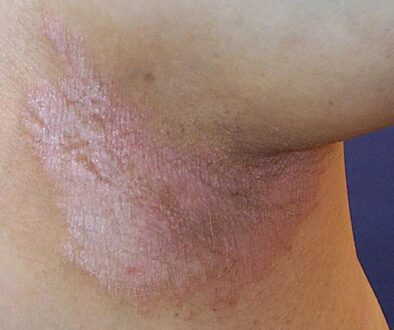
It is possible that the pigment loss occurs in people who have suffered from various types of skin damage. This is often seen in those who had ulcers or blisters, as well as in burn patients or in those who suffered from bacterial skin infections. Basically, the skin fails to replace the loss pigment in the damaged area, which results in hypopigmentation. No treatment is available for such problems, but there are creams that can be used to even out the skin tone.
Vitiligo, common cause of pigment loss
When a person suffers from vitiligo, it means that the melanocytes at the level of the skin are not functioning properly. These are either dysfunctional or they are lost altogether, leading to the appearance of white patches on the skin, with a characteristic smooth texture. The skin is more sensitive in those areas, due to the fact that it lacks the necessary melanin for protection.
Unfortunately, vitiligo cannot be cured. Patients are advised to cover the white patches on the skin; they can undergo ultraviolet light therapy or use corticosteroid topical treatments. An extreme solution is the depigmentation of the skin that has remained unaffected by the loss of pigment.
These are some of the most common skin pigmentation disorder. Because some of these cannot be cured, many patients fight with feelings of low self-esteem, anger, and frustration, requiring psychological counseling to deal with their feelings and cope with the condition.