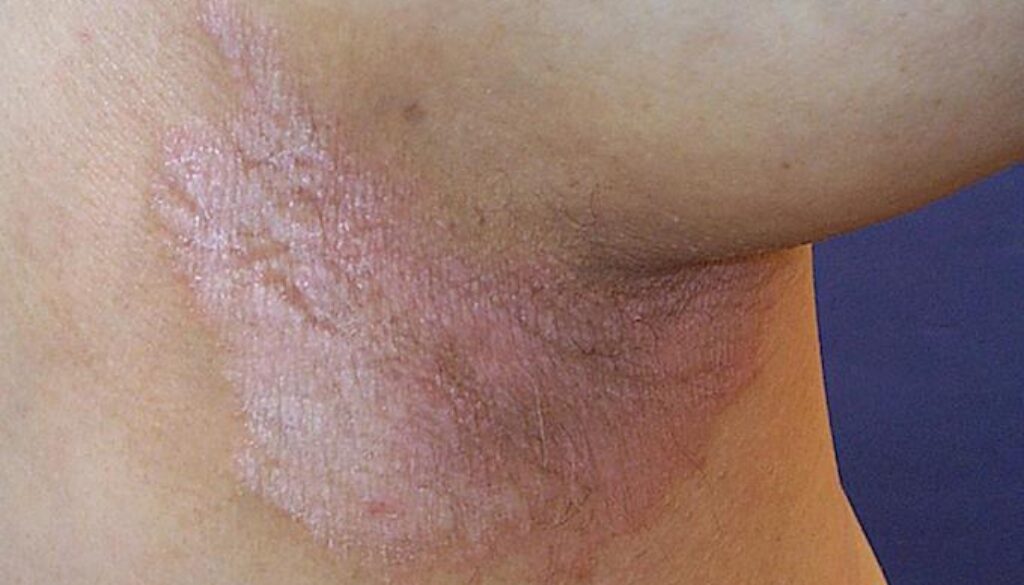
Jock Itch (Tinea Cruris) in Women: Causes, Precautions, and Treatment
Introduction
Often mistakenly believed to predominantly affect men, Tinea cruris, more commonly known as jock itch, is a skin condition that can equally impact women. Although the name might suggest a more sports-related condition, it’s not exclusive to athletes or “jocks.” This skin condition is a type of fungal infection, causing discomfort in the region of the groin, the inner portions of the thighs, and occasionally, even the buttocks. It’s characterized by redness, itching, and a rash. As such, understanding the causes, preventive measures, and treatment options is essential for those who might encounter it.
Causes of Tinea Cruris in Women
Jock itch is primarily caused by a group of fungi known as dermatophytes. These organisms are naturally present on the skin and generally cause no harm. However, given the right conditions, these fungi can overgrow, leading to a fungal infection. Warm, moist areas are particularly prone to such infections, which is why the groin and inner thigh regions are often affected.
While both men and women can develop jock itch, women might encounter this condition due to several factors:
- Sweating and Humidity: The propensity of the groin area to sweat, combined with natural body warmth, provides an optimal environment for fungal growth.
- Wearing Tight Clothes: Tight clothing, especially underwear made from non-breathable materials, can trap moisture, promoting fungal overgrowth.
- Obesity: Increased skin folds can trap warmth and moisture, again providing a conducive environment for the fungi.
- Immunosuppression: Women with weakened immune systems due to conditions such as diabetes, HIV/AIDS, or those undergoing immunosuppressive treatments are more susceptible to jock itch.
- Sharing Personal Items: Using shared personal items like towels or clothes can also lead to transmission of the fungi.
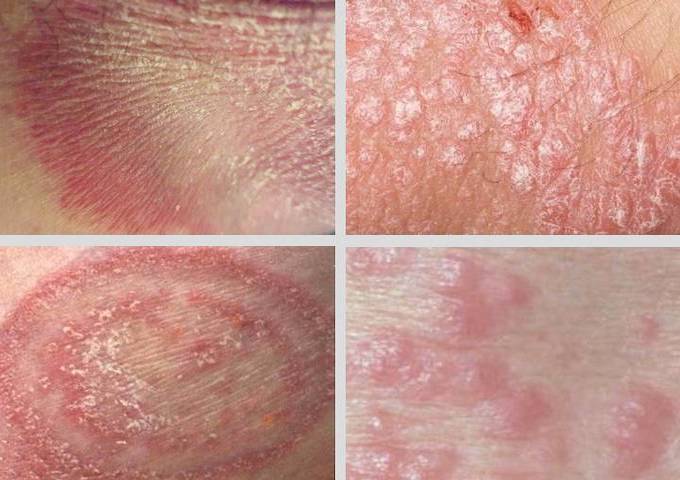
Precautions Against Tinea Cruris
Adopting several preventive measures can significantly decrease the likelihood of developing jock itch. They include:
- Personal Hygiene: Regular bathing, particularly after sweating or exercise, can help keep the skin clean and reduce the risk of fungal overgrowth.
- Proper Clothing: Opt for loose-fitting, breathable clothing, especially underwear. This helps reduce sweating and keeps the area dry.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Personal items like towels and clothes should not be shared to avoid the transmission of fungi.
- Drying Off Completely: After bathing or swimming, ensure to dry off completely, particularly in the groin area, as dampness can encourage fungal growth.
- Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet and regular exercise can help strengthen the immune system, reducing the susceptibility to infections.
Treatment of Tinea Cruris in Women
Jock itch, despite causing discomfort, is typically not a serious condition and can be treated effectively. There are two main categories of treatment – medical and herbal.
Herbal Treatment:
Several natural or herbal remedies have been suggested for treating jock itch. These remedies often have antifungal properties and can serve as alternatives for individuals who prefer a more natural approach.
- Tea Tree Oil: Known for its antifungal and antibacterial properties, tea tree oil can be applied to the affected area using a cotton pad. It’s crucial to dilute the oil with a carrier oil like coconut oil to prevent skin irritation.
- Garlic: Garlic has potent antifungal properties. Crushed garlic can be applied directly to the skin or consumed as part of the diet.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Diluted apple cider vinegar can help kill fungi due to its acidic nature. It can be applied to the skin using a clean cloth or taken orally.
- Aloe Vera: Famous for its healing properties, aloe vera can soothe the itching and discomfort associated with jock itch. Aloe vera gel can be directly applied to the skin.
- Coconut Oil: This versatile oil has natural antifungal properties and can be applied directly to the affected area. It not only fights the infection but also soothes the skin and reduces itching.
- Turmeric: Known for its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, turmeric can be used topically or orally. For topical application, make a paste of turmeric powder with water and apply it to the affected area. Alternatively, you can drink turmeric milk or take curcumin (the active ingredient in turmeric) supplements.
- Oregano Oil: This essential oil is known for its antifungal and antibacterial properties. Remember to dilute it with a carrier oil before applying to the skin to prevent irritation.
- Neem: Often referred to as an “all-purpose” plant, neem has potent antifungal properties. A paste made from neem leaves can be applied to the affected area. Additionally, bathing with neem-infused water can also provide relief.
- Lavender Oil: Apart from its calming aroma, lavender oil has antimicrobial properties. Combine it with a carrier oil and apply it to the affected area.
- Licorice: This root has over 25 antifungal compounds. You can prepare a tea with licorice root and apply it to the affected area using a clean cloth.
- Echinacea: This herb is known for its immune-boosting properties. Topical creams containing Echinacea can be applied to the infected area.
- Chamomile: Chamomile has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. Chamomile tea can be applied topically with a clean cloth, or a chamomile cream or ointment can be used.
Remember, while these natural remedies are generally safe, everyone’s body reacts differently. What works well for one person may not work as well for another. Always perform a patch test when trying a new topical treatment to ensure you don’t have an adverse reaction. Moreover, these remedies are intended to supplement, not replace, medical treatments. It’s important to seek professional medical advice if symptoms persist or worsen despite home treatment.
Medical Treatment:
Medical treatment for jock itch primarily involves antifungal medications. They are available in various forms, such as creams, powders, and sometimes oral medication.
- Topical Antifungals: Over-the-counter antifungal creams, ointments, or sprays are commonly used to treat jock itch. They include miconazole, clotrimazole, and terbinafine.
- Oral Antifungals: For more severe or persistent cases, healthcare providers might prescribe oral antifungal medications such as fluconazole or itraconazole.
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any medical treatment, as these treatments may have side effects or may interact with other medications you might be taking.
Conclusion
Jock itch, while potentially uncomfortable and embarrassing, is a treatable condition. Proper understanding of the causes, effective preventive measures, and appropriate treatment options, whether medical or herbal, can aid in managing this condition. As always, personal hygiene and a healthy lifestyle play a critical role in preventing such infections. Regular consultations with healthcare providers can ensure that jock itch or any other health concerns are diagnosed and treated promptly, leading to a healthier, more comfortable life.